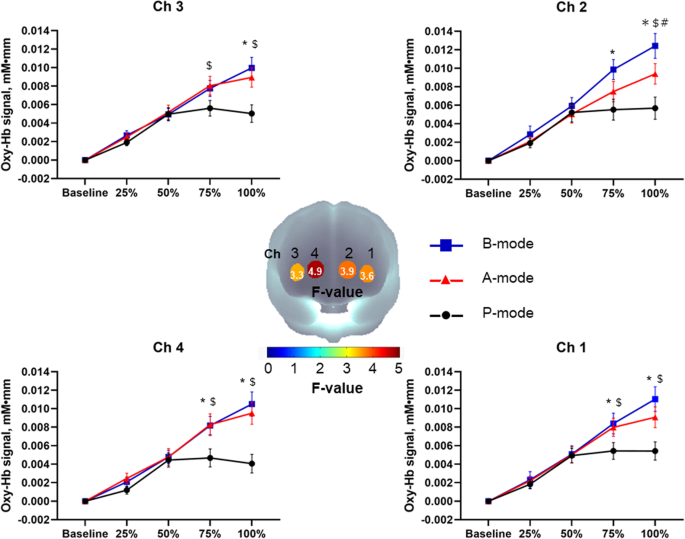
・This study examined the effects of home-based manual dexterity training on cognitive function in older adults. We also assessed the cortical activation patterns (cognitive load) of the prefrontal cortex to quantify the cognitive load via a wearable device.
・The results confirmed that the higher the difficulty of the training, the greater the cerebral blood flow in the prefrontal cortex, and among cognitive functions, executive function improved significantly in the intervention group compared to the control group. The training group also showed larger effect sizes for cognitive functions other than executive functions.
・Our study suggests that manual dexterity training can improve performance in a complex manual dexterity task and executive functioning in older adults.
-
最近の投稿
アーカイブ
カテゴリー