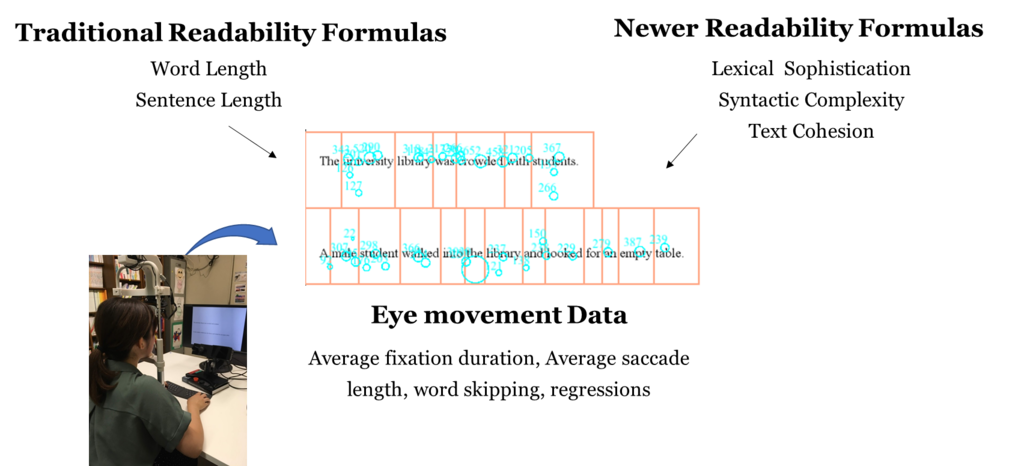
・Eye movement data provides four direct measures of processing effort involved during reading: (1) The time spent fixating on words between eye movements, (2) the length of the movements, (3) the frequency of skipping words, and (4) the frequency of regressive eye movements back to previously read text.
・Several existing readability formulas can be used to predict processing effort, as evidenced by eye movements during reading to some extent.
Abstract
Although text readability has traditionally been measured based on simple linguistic features, recent studies have employed natural language processing techniques to develop new readability formulas that better represent theoretical accounts of reading processes. This study evaluated the construct validity of different readability formulas, including both traditional and newer formulas, by examining their ability to predict the processing effort involved during L2 reading as evidenced by eye movements. Two studies (an experimental study and a corpus-based study) were conducted in which the readability of target texts was calculated using different formulas and then utilized to develop models that predict particular eye movement patterns during reading. These studies revealed that although traditional formulas showed reliable performance in predicting particular eye movement patterns, in many cases, the newer formulas outperformed them. These findings support the newer readability formulas as more theoretically valid and accurate measures of the processing effort involved in L2 reading.
Benefit
Newer readability formulas that consider the cognitive aspects of reading are more accurate than the traditional models at assessing reading effort in English second language. However, no single formula is the best on all measures. When evaluating text for reading effort, a combination of formulas is likely to be the best strategy.
Market Application
Online education, L2 Textbook, Smart glass
Publications
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/lang.12455
Other
https://www.tsukuba.ac.jp/en/research-news/20210927140001.html